Introduction to Flutter Fleas
Fluttering about in the water column are animals barley visible to the naked eye. These jitterbugging planktonic organisms are known as flutter fleas and they are found in great numbers. Unique to this specimen is their lengthy biramous arms containing setae that assist them in swimming and capturing prey.
Lifestyle and Habitat
Diet:
Flutter fleas are heterotrophs that feed on any organism in the water column that is smaller then them in size. To digest prey flutter fleas have a proboscis that is housed under their cephalosome. When a planktonic organism such as a larval form from a benthic or pelagic species floats near, the flutter flea exerts all of its energy to jut forward and capture its victim. The prey item is held in front of the creature and the proboscis brushes against the superficial membrane of the captured organism. Enzymes are excreted that break down the outer membrane which allows the proboscis access to the tender inner organs.
Species
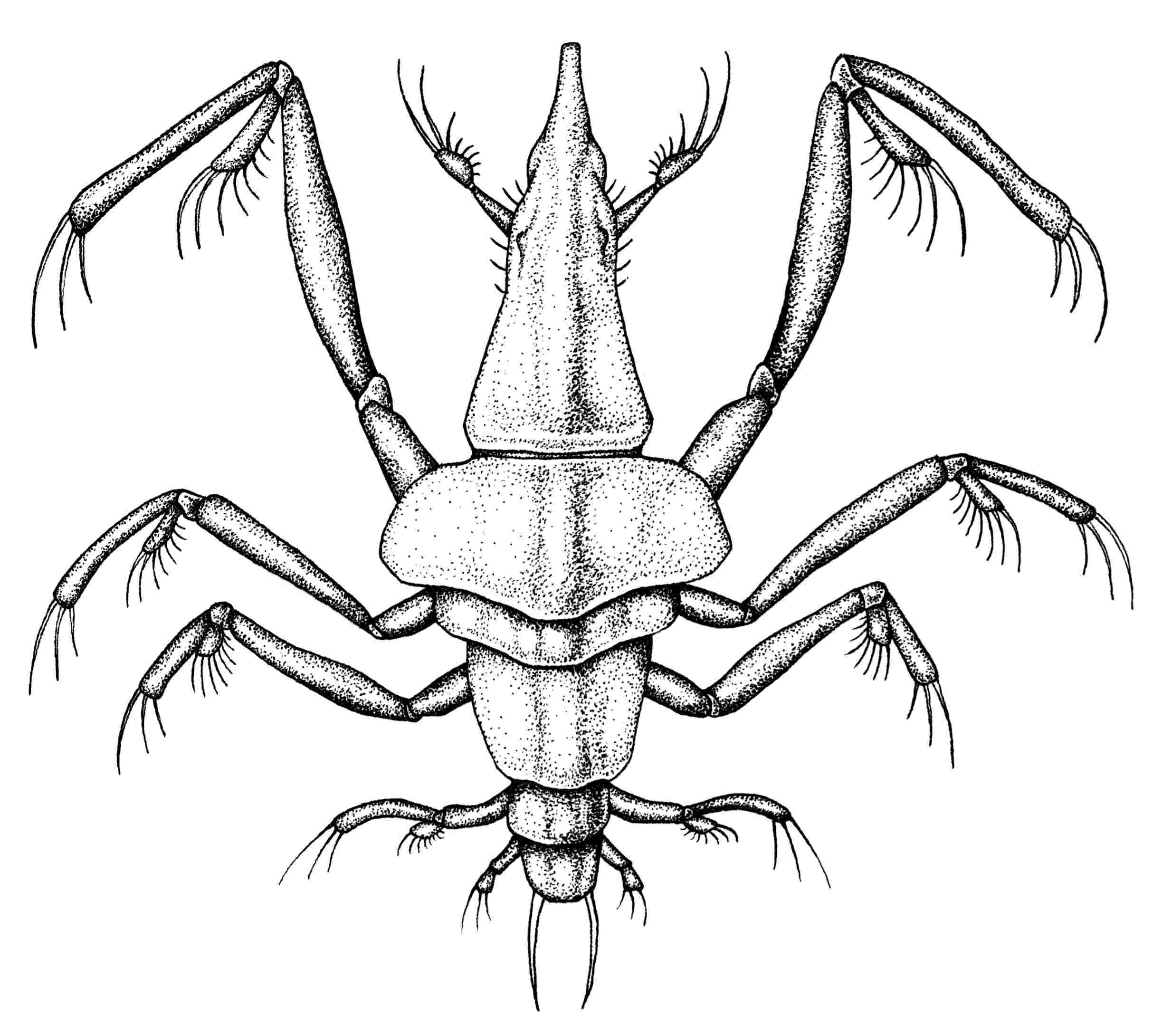
Cephalopipa hermes
Common Name: Hermian flutter flea
Diet: Motile larvae and other plankton
Size: 1mm–4mm
Description: C. hermes float low in the water column. Their cephalosomes point upwards and fixate on any form of movement above. When a smal larval organism passes overhead C. hermes lunges out, using its powerful legs to swiftly ambush prey. Their first raptorial limb tightly grasps prey items and allows its proboscis ample time to liquefy and ingest innards.
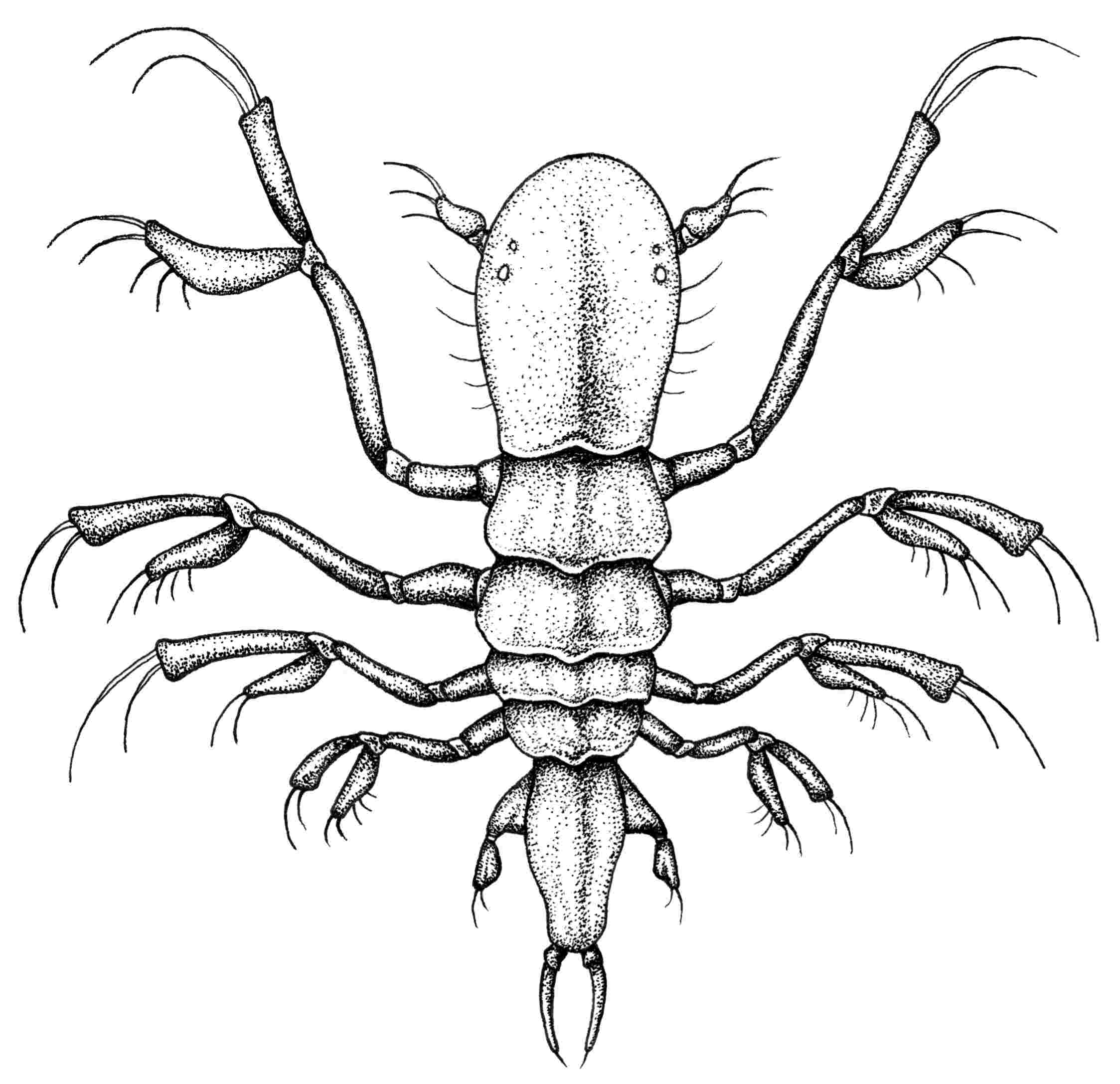
Cephalorotundus dumbo
Common Name(s): Eared flutter flea or microtia flutter flea
Diet: Motile phytoplankton
Size: 1mm–4.2mm
Description: C. dumbo has enlarged eye spots that aid in locating food items. The species preys on motile phytoplankton of specific yellow and orange hues. The reason why is unknown but it is suggested that intense competition between flutter fleas caused certain species to prioritize a particular organism.
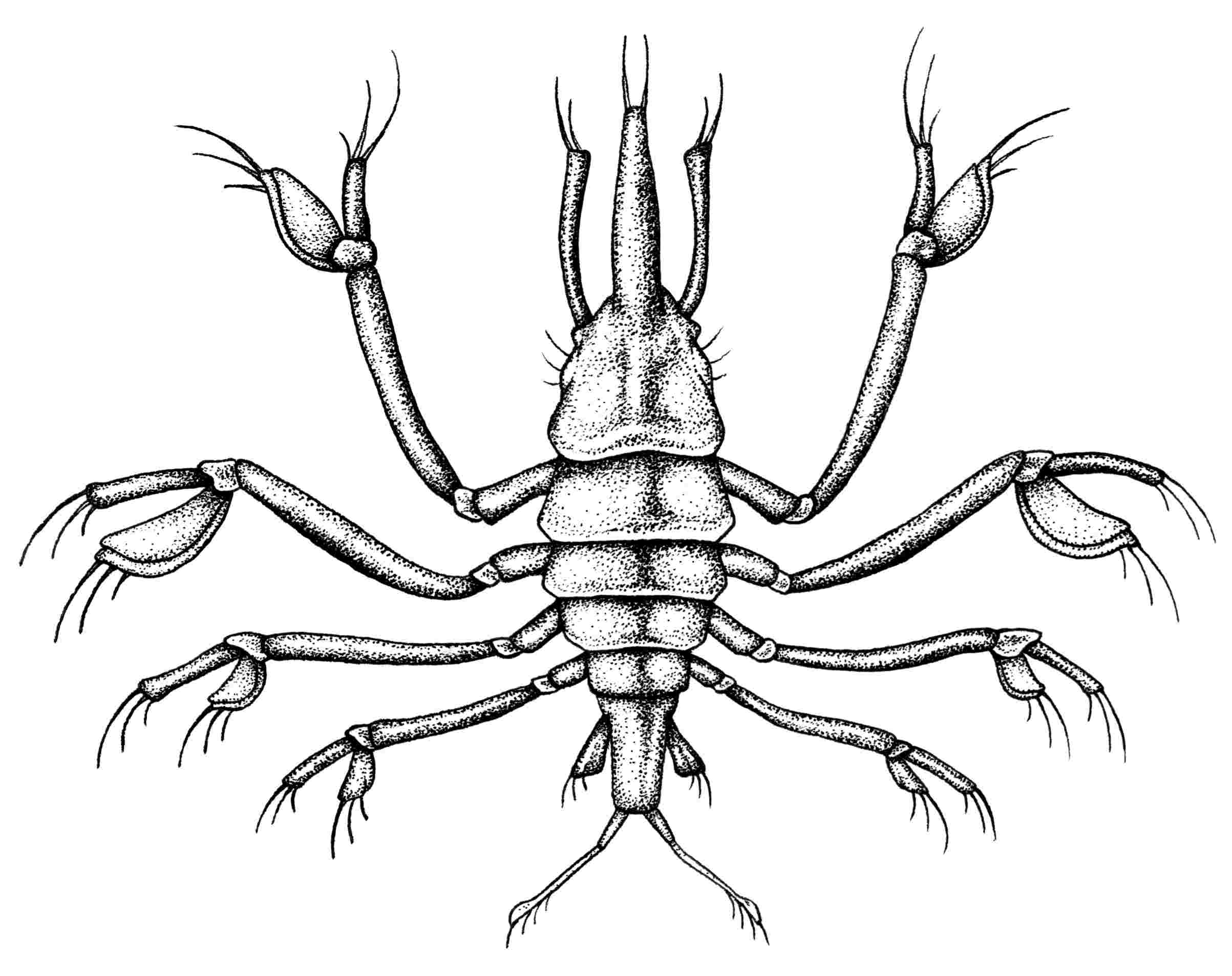
Faciatridens padela
Common Name: Trident flutter flea
Diet: Motile plankton and phytoplankton
Size: 1mm–3.1mm
Description: F. padela posses an unusual rostrum that most likely aids in locating prey. The expodites on each leg are flattened and assist in maneuverability. Additionally this species of flutter flea exhibits bioluminecence, primary located in the expodites.